Intrinsic Impedance
The intrinsic impedance is a property of a medium - an area of space. For a vacuum (outer space) or for
wave propagation through the air around earth (often called 'free space'), the intrinsic impedance
(often written as
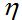 or Z)
is given by:
or Z)
is given by:
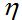 =
= This parameter is the ratio of the magnitude of the E-field to the magnitude of the H-field for a plane wave in a lossless medium (zero conductivity):

This relation can be derived directly from
Maxwell's Equations. For a
general medium with permittivity and permeability given by

For a medium with a conductivity
 When the conductivity is non-zero, the above intrinsic impedance is a complex number, indicating that the electric and magnetic fields are not in-phase. The intrinsic impedance of free-space has nothing to do with the electrical impedance of an antenna. Also, there is no reason to have the impedance of an antenna match the intrinsic impedance of free space (no mismatch loss occurs).
|

Custom Search
|
Antennas (Home)
 , the intrinsic impedance is given by:
, the intrinsic impedance is given by: associated with it, the
intrinsic impedance is given by:
associated with it, the
intrinsic impedance is given by: